Digestion & Absorption

Catalytic Proteins
Enzymes selectively accelerate each step in metabolism (enzymes are regulated)
Catabolic Pathways - release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler molecules (energy is stored in cell for future use)
Anabolic Pathways - consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler compounds (energy from catabolic pathways is used)
Structures within the cell bring order to metabolic pathways
A team of enzymes for several steps of a metabolic pathway may be assembled together as a multienzyme complex
The product from the first can then pass quickly to the next enzyme until the final product is released
Overview of GI System
-
Movement
-
Secretion
-
Digestion
-
Absorption
-
Elimination
-
Nutrient production by intestinal bacteria
Digestion = hydrolysis
- break bonds by adding water
- break large molecules in foods into smaller molecules
Absorption = transport or transfer of the products of digestion into blood
- blood will carry molecules to cells

Tightly controlled and regulated
GI Structure
GI stretches from mouth to anus
Common Features (not the mouth)
-
concetric circles of tissues
-
same layers regardless of location
-
muscles
-
cells (secretion)
-
blood vessels
-
nerves
-
emphasis varies with respect to which layer functions in which location
-

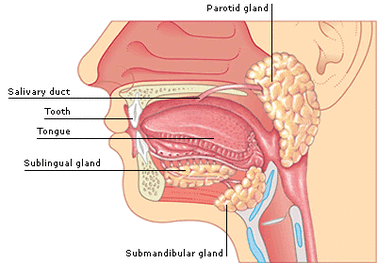
Mouth
-
Glands produce saliva
-
saliva contains enzymes that break down starch and lipids and mucus that lubricates food
-
contains lyzozyme that kills bacteria
-
-
chewing breaks food into smaller pieces
-
increases surface area, allowing enzymes to have greater access
-
-
tongue has taste receptors
-
food enters the stomach via esophagus
Esophagus
-
very muscular
-
forces food into stomach
-
at the top of the esophagus is a valve-like flap called the epiglottis (prevents food from entering trachea)
-
food also gets down esophagus by muscular contractions (peristalsis) and gravity

Stomach
-
2-3 distinct regions
-
upper - fundus
-
stretchy
-
storage
-
-
middle - body
-
empty ≈ 2oz
-
full ≈ 1-1.5L
-
-
lower - pylorus
-
mix and propel
-
-
-
processes swallowed food in a preliminary manner for delivery into SI
-
secretes acids and enzymes
-
-
food usually stays in for 2-3 hours
-
solids take longer than liquids
-
fatty meal takes longer than protein or CHO
-



Small Intestine
-
small because of diameter, not length
-
three regions
-
duodenum (first foot)
-
jejunum (next 4 feet)
-
ileum (last 5 feet)
-
-
most digestion completed in the jejunum with help from enzymes (from intestinal cells and pancreas)
-
muscular contractions mix food
-
-
attaches to colon (large intestine)

-
increases surface area to facilitate digestion and absorption of nutrients
-
mucosa are folded into villi -finger - like projections
-
villi have microvilli that make up the brush border membrane of the absorptive cells
-
increases surface area 600x
-
-
the absorptive cells that have this brush border membrane are called enterocytes

Accessory Organs
LIVER
-
makes bile (needed for lipid digestion)
GALLBLADDER
-
stores/concentrates bile
-
bile duct connected to SI
PANCREAS
-
exocrine - secretes through ducts
-
secretes HCO3 (to neutralize H+)
-
secretes enzymes
-
enter via pancreatic duct
-
-
endocrine - secretes directly into blood
-
insulin and glucagon
-
both made in the islets of langerhans
-

Colon (large GI)
-
measures 3.5ft
-
separated into 5 sections
-
contains bacteria, which may digest some escape CHO and fiber
-
synthesizes vitamin B12 and K (absorbed in colon)
-
-
little digestion happens here
-
95% occurs in SI
-
-
contents remain for 24-72 hours
-
reabsorption of water and compaction of chyme into feces and storage of fecal matter

Regulation of Digestion (neural and hormonal)
NEURAL
-
faster
-
nerves line walls of GI tract
-
exist in networks or plexus
-
receive messages from stimuli
-
food
-
pressure
-
acid
-
-
response
-
contraction
-
secretion
-
HORMONAL
-
most sustained
-
via regulatory pipes
-
4 main ones
-
each has a main function
-
1 made in stomach (gastrin)
-
3 made in duodenum
-
CCK
-
secretin
-
GIP
-
-
-
In response to chyme
-
release peptides -> blood -> target organ -> action
-

ROLE OF HORMONES
-
gastrin
-
chyme -> stomach cells -> release gastrin -> parietal cells -> HCl
-
-
secretin
-
stimulates pancreas to release HCO3
-
stimulates liver to secrete bile to gallbladder
-
HCO3 counteracts the acidity of chyme and raises the pH so enzymes can function properly
-
-
CCK
-
released in response to
-
partially hydrolyzed fat
-
proteins
-
acidic pH of chyme
-
-
stimulates gall bladder to contract and release bile
-
stimulates release of a secretion from the pancreas
-
contains digestive enzymes and proenzymes
-
these enzymes work best at neutral pH, where HCO3 comes in
-
-

Major Digestive Enzymes
MOUTH
-
salivary amilase
-
secreted by salivary glands
-
works on starch and glycogen
-
end-product = maltose
-
-
lingual lipase
PANCREAS
-
enzymes made and secreted by the pancreas
-
active
-
pancreatic amylase
-
acts on starch, glycogen
-
-
pancreatic lipase
-
acts on TGs and cholesterol
-
-
-
inactive
-
packaged in pancreas as zymogens
-
CCK stimulates
-
inactive zymogens secreted into SI
-
activated in SI
-
digest proteins
-
-
STOMACH
-
pepsin
-
activated by gastric acidity
-
pepsinogen -> pepsin
-
works on protein
-
end product = large peptide fragments and peptones
-
-
gastric lipase
-
acts on short chain and medium chain TGs
-
end-product = FAs and monoglycerides
-
INTESTINE
-
Enterokinase
-
involved in protein digestion (activates trypsin)
-
-
digestion completed by intestinal enzymes at brush border membrane of enterocytes
-
aminopeptidase
-
peptides -> amino acids
-
-
disaccharidases
-
work on sucrose, maltose and lactose
-

Overview




